EDITORIAL
Abstract book of the XXXIV Russian Symposium on Surgical Endocrinology "Kalinin readings"
Original study
BACKGROUND: An increase in the number of patients with thyroid nodules necessitates a detailed study of diagnostic capabilities that improve the quality of their preoperative verification and the choice of optimal treatment tactics. In this regard, the active improvement and introduction of new high-tech techniques continues, which require justification of the effectiveness of their use in clinical practice.
AIM: To develop an integrated diagnostic scale for assessing the risk of malignancy of thyroid nodules, contributing to the choice of the optimal surgical treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: To assess the validity of the treatment and diagnostic tactics and select the optimal volume of surgical intervention with the development of an original integral diagnostic scale, a retrospective analysis of the results of the examination and treatment of 244 patients with thyroid nodules, as well as a prospective study, including 65 clinical observations, was carried out.
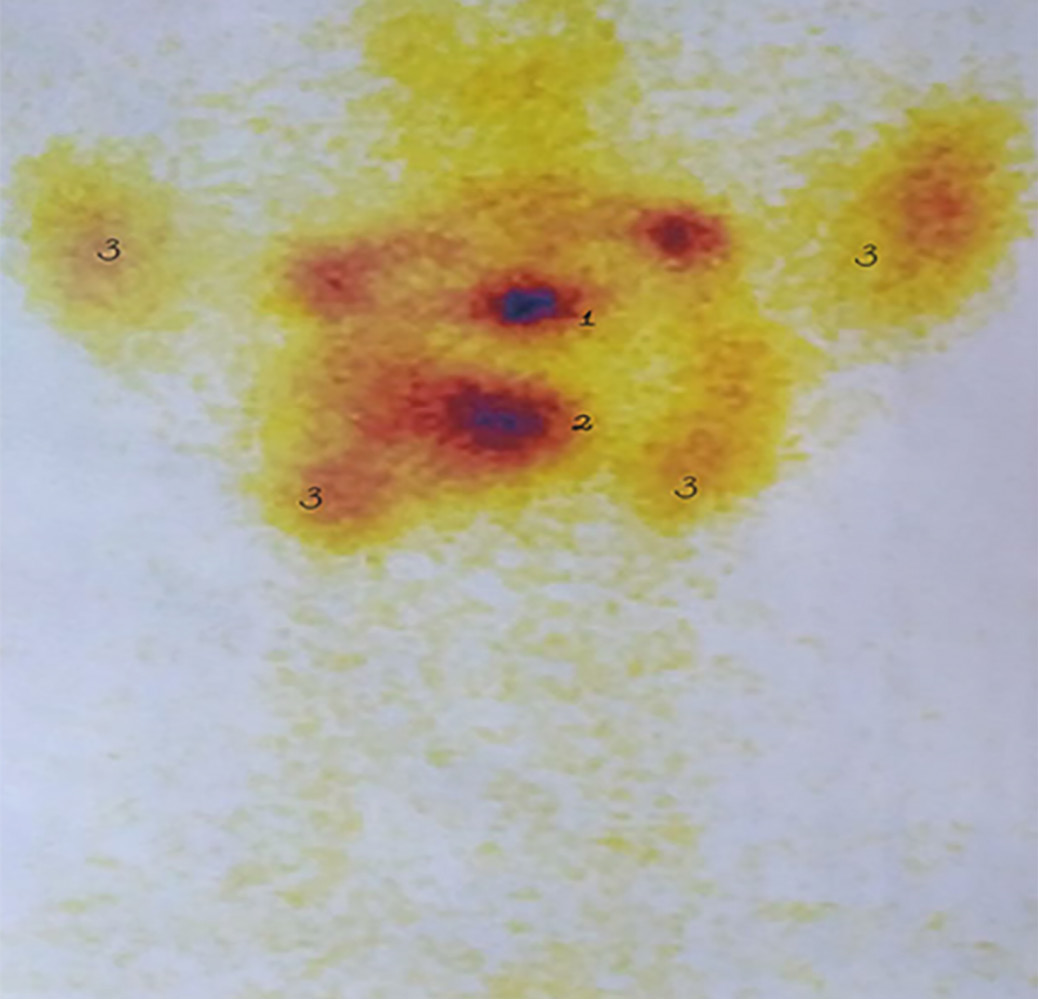
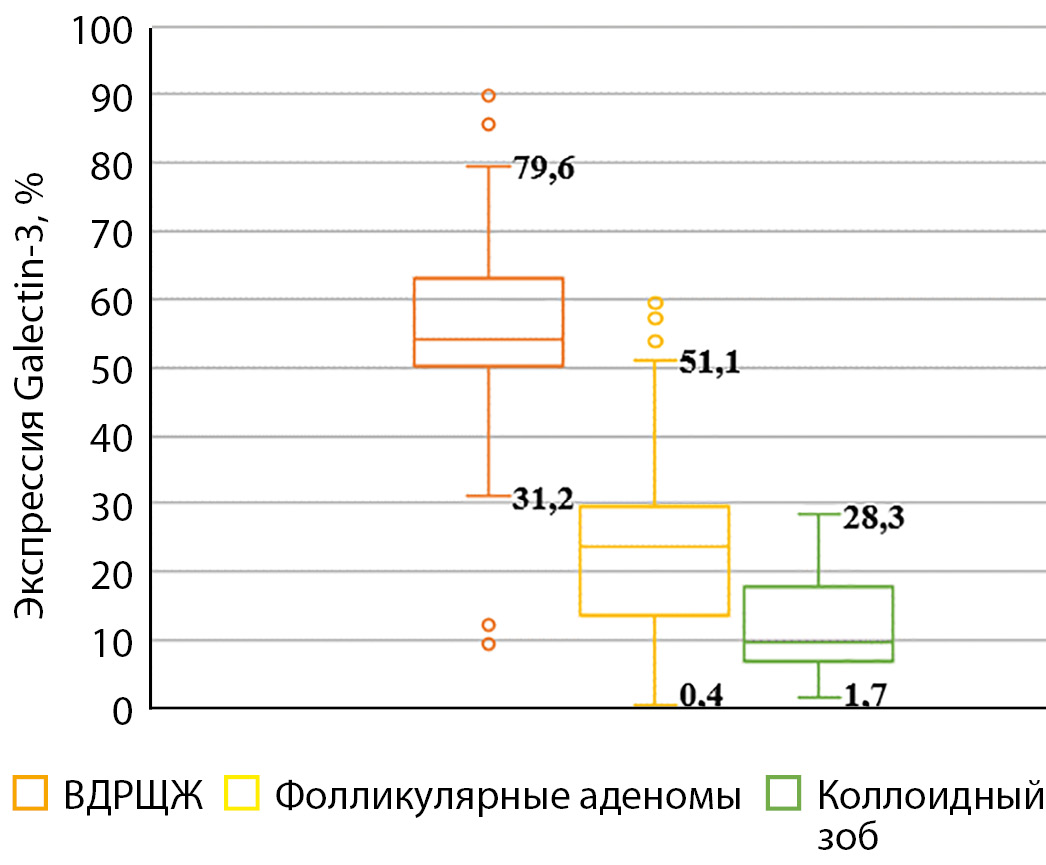
RESULTS: In the course of the study, a systematic approach to the differential diagnosis of thyroid nodules was implemented using the most effective modern methods of laboratory and instrumental examination as part of the development of an original integral scale. It has been proven that the use of an integrated diagnostic scale allows predicting the risk of malignancy of formations: low (3–7%) with 0–5 points, medium (7–35%) — 6–10, increased (35–80%) — 11–15, high (80–96%) — 16–20. It has been established that in patients with an increased and high risk of malignancy, the diagnostic accuracy of the proposed integrated scale in detecting highly differentiated thyroid cancer increases to 90.2% when determining the expression of Galectin-3 above 31.2% in the puncture material, as well as in papillary carcinoma — up to 100% when the BRAF V600E mutation is detected. The treatment and diagnostic algorithm for clinical use has been optimized, allowing individualization of treatment tactics: for patients with an increased and high risk of malignancy, it is advisable to perform thyroidectomy with central lymphadenectomy; with an average risk — hemithyroidectomy; with low risk in the absence of signs of compression of the neck organs — dynamic observation, and if it is present — resection of the thyroid gland. It is shown that the implementation of a modified diagnostic and treatment algorithm, taking into account the use of an integral diagnostic scale, provides good immediate results of treatment.
CONCLUSION: The introduction of an improved diagnostic and treatment algorithm, taking into account the use of an integrated scale for a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental assessment of thyroid nodules, makes it possible to increase the efficiency of their preoperative differential diagnosis and to choose an individualized surgical treatment option.
BACKGROUND: According to the literature, there are contradictory results regarding the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without contrast enhancement (CE) in insulinoma, and studies that analyze the factors influencing the obtaining of false negative results have not been described.
AIM: Evaluation of the operational characteristics of MRI imaging of insulinoma without CE.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Imaging studies of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space were performed in patients with suspected nondiabetic hypoglycemia (NDH): MRI without CE (index test) and CT with CE (first row reference test). Ultrasound examination was used as a reference test of the second row, and arteriostimulated venous blood sampling was used in the third row. The diagnosis of NDH and insulinoma was established based on the detection of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia during laboratory examination and confirmation of the presence of a pancreatic tumor.
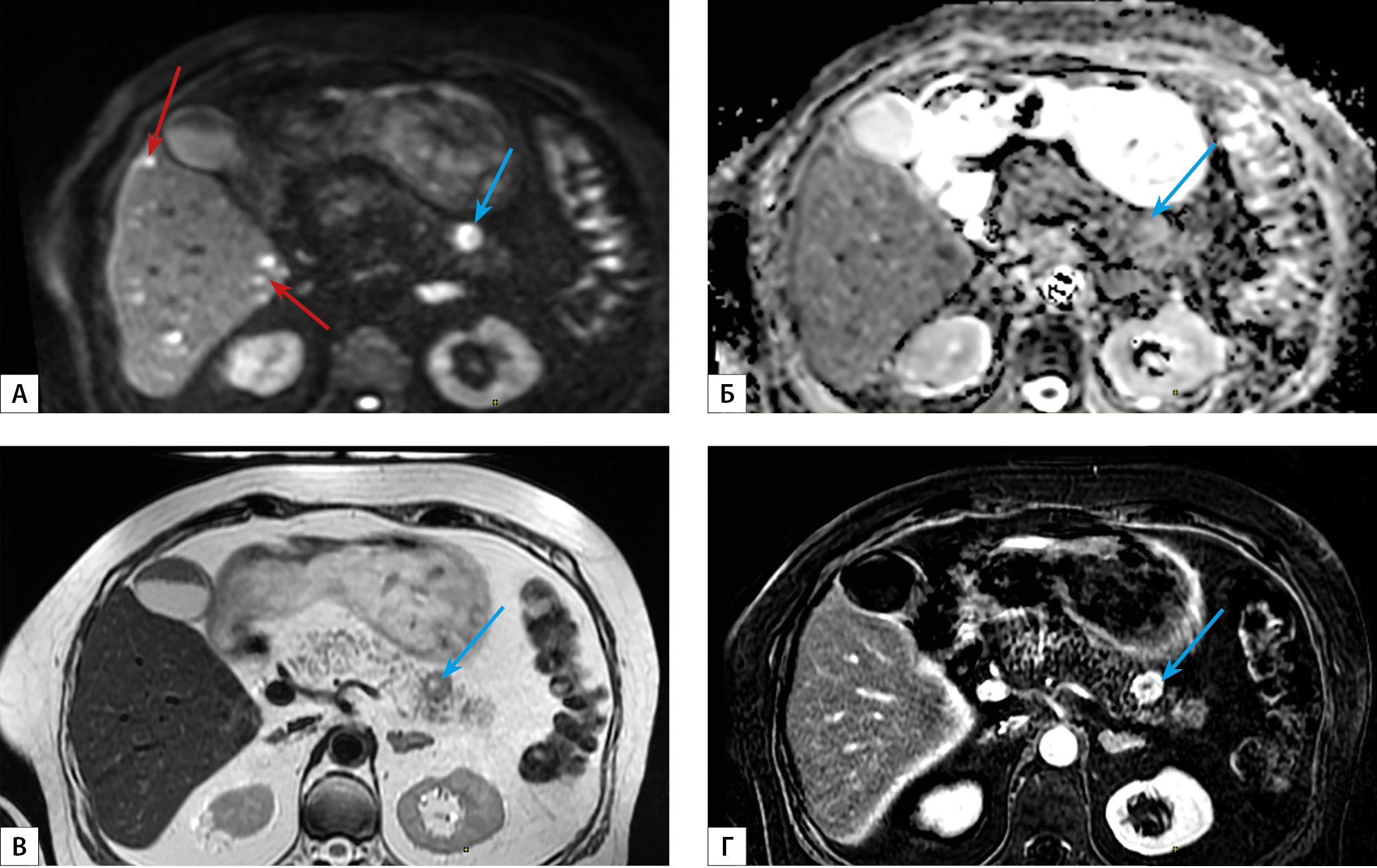
RESULTS: 125 patients with insulinoma and 55 patients with other causes of NDH were included. The sensitivity of MRI without CE in the diagnosis of insulinoma was 94%, 95% CI [89%; 98%], specificity — 98%, 95% CI [90%; 100%], prognostic value of a positive result — 99%, 95% CI [95%; 100%], prognostic value of a negative result is 87%, 95% CI [76%; 94%]. The Kappa index of agreement with the final diagnosis was 0.886 (95% CI [0.814; 0.958]), which corresponds to excellent agreement, with CT — 0.750 (95% CI [0.651; 0.850]), which corresponds to significant agreement.
In a comparative analysis of the tomographic and pathomorphological characteristics of insulinoma, in cases with divergent results when using MRI without CE and CT with CE, significant differences in structure, shape, contour features, localization and degree of malignancy of the tumor, as well as the structure of its surrounding parenchyma were not revealed.
In the presented sample, the insulinoma has a median size of 14–15 mm with the median optical density in the native phase of CT 42–44 units.H, hyperintensivity on T2-weighted MRI images in 89%, 95% CI [78%; 95%] cases and low Grade 1 malignancy in 70%, 95% CI [56%; 81%] cases.
CONCLUSION: CT with CE and MRI without CE are characterized by significant agreement in the diagnosis of insulinoma. In this regard, as well as due to the lack of radiation exposure and the strict need for contrast agents, MRI without CE can be recommended as a first-line method on a par with abdominal ultrasound and CT with CE to detect insulinoma.
Clinical Case
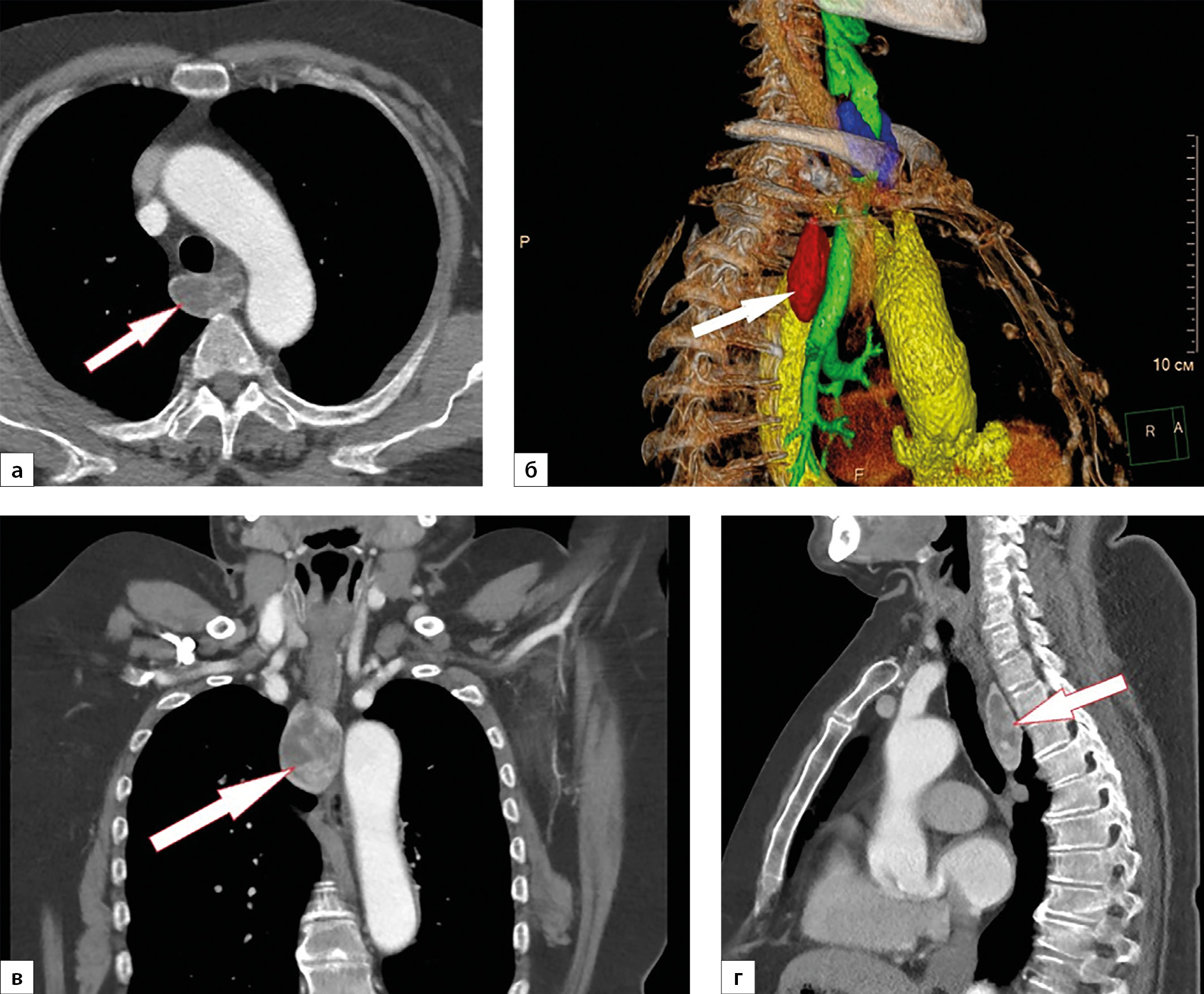
Recently, primary hyperparathyroidism, which represents a medical and socially significant problem, has become increasingly relevant. The high prevalence of forms without pronounced clinical symptoms, as well as the low awareness of doctors regarding this pathology, lead to late diagnosis, delayed initiation of treatment and, as a consequence, the development of serious multisystem complications with a higher risk of premature death. At the same time, early diagnosis is based on relatively laboratory tests — serum calcium and parathyroid hormone, and visualization of the adenoma in most cases is provided by ultrasound examination and scintigraphy. This article is a case report of primary hyperparathyroidism caused by an ectopic parathyroid adenoma located in the mediastinum, when late treatment led to the patient’s long-term suffering and the development of severe complications.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2310-3965 (Online)